In today's digital era, the landscape of cyber threats is rapidly evolving, becoming more frequent and sophisticated.
In 2022, 70% of businesses were victims of ransomware attacks, highlighting the urgent need for robust security measures. Over 80% of cyber attacks are preventable with proper software and patch updates.
Online threats underscore the critical role patch management plays in safeguarding against these dangers.
In this article, we’ll talk about why cyber attacks are increasing, the different types of cyber attacks, the role patch management in cyber security, and much more.
Why Cyber Threats Are Increasing
With the rapid technological advances, cyber attacks are far from extinct. It’s up to each business to implement the proper preventative measures to ensure the security of their company resources. But first, it's important to understand why cyber threats are on the rise.
The surge in cyber threats can be attributed to several key factors:
- Increasing reliance on digital technologies
- Shifting to remote work
- Sophisticated cybercriminals exploiting advanced techniques to breach defenses
- Poor awareness or security training
- Vulnerabilities in supply chain infrastructure
- Value of stolen data from data breaches
- Rise of ransomware
- IT industry’s rapidly changing environment
Inadequate workspace security measures often fail to keep pace with these evolving threats and a significant contributor to this vulnerability is unpatched software.
Over 60% of cyber attacks didn’t apply a security patch where one was available. This underscores the critical role of timely patch management in mitigating cyber threats. Maintaining updated systems can significantly reduce the risk of a successful cyber attack, highlighting the importance of proactive cybersecurity practices.
For the most current statistics and insights, please refer to the official Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) website and their cybersecurity research reports.
Understanding and Identifying Cyber Threats
Understanding the landscape of cyber threats is essential for safeguarding our virtual and real-world assets.
Cyber threats come in various forms, each with its unique methods and devastating consequences. Here are some of the main threats a business may be vulnerable to:
- Exploit attacks: exploits take advantage of known vulnerabilities in software or systems that neglected patches or updates. Through these vulnerabilities, attackers gain unauthorized access or perform unauthorized actions.
- Zero-Day attacks: when attackers exploit a previously unknown vulnerability in software or hardware before the developers have released a patch for it
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks: when outdated software has vulnerabilities that make MitM attacks easier. Attackers intercept and alter communication between two parties without their knowledge, often exploiting weaknesses in encryption.
- SQL Injection attacks: exploit vulnerabilities in web applications that use SQL databases. Attackers insert or "inject" malicious SQL queries into an input field to gain access to or manipulate the database.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks: occurs when attackers inject malicious scripts into content from otherwise trusted websites
- Drive-by downloads: exploits vulnerabilities in browsers, plugins, or software to install malicious software without the user's knowledge
The common thread for these threats is they often target vulnerabilities that can be easily mitigated through diligent patch management. Regularly updating systems, applications, and software with the latest security patches is one of the most effective measures to protect against a wide range of cyber threats.
4 Real-World Cyber Threat Examples
To help understand the cyber threats all companies are susceptible to, here are a few examples of large companies who have fallen victim to online attacks.
- The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 impacted over 200,000 computers across 150 countries, crippling healthcare systems, and causing billions in damages
- A major phishing scam targeted Google and Facebook between 2013 and 2015, where a hacker masquerading as a computer-parts supplier conned the companies out of over $100 million
- In 2016, the Dyn cyber attack, a large-scale DoS attack, disrupted major websites like Twitter, Netflix, and PayPal, showcasing the vulnerabilities in our interconnected networks
- In 2023, China’s largest bank, ICBC, was hit with a major ransomware attack that disrupted its financial service systems.
By understanding the types of threats and their potential impacts, individuals and organizations can better prepare and protect themselves against the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.
What is the Cost of a Data Breach?
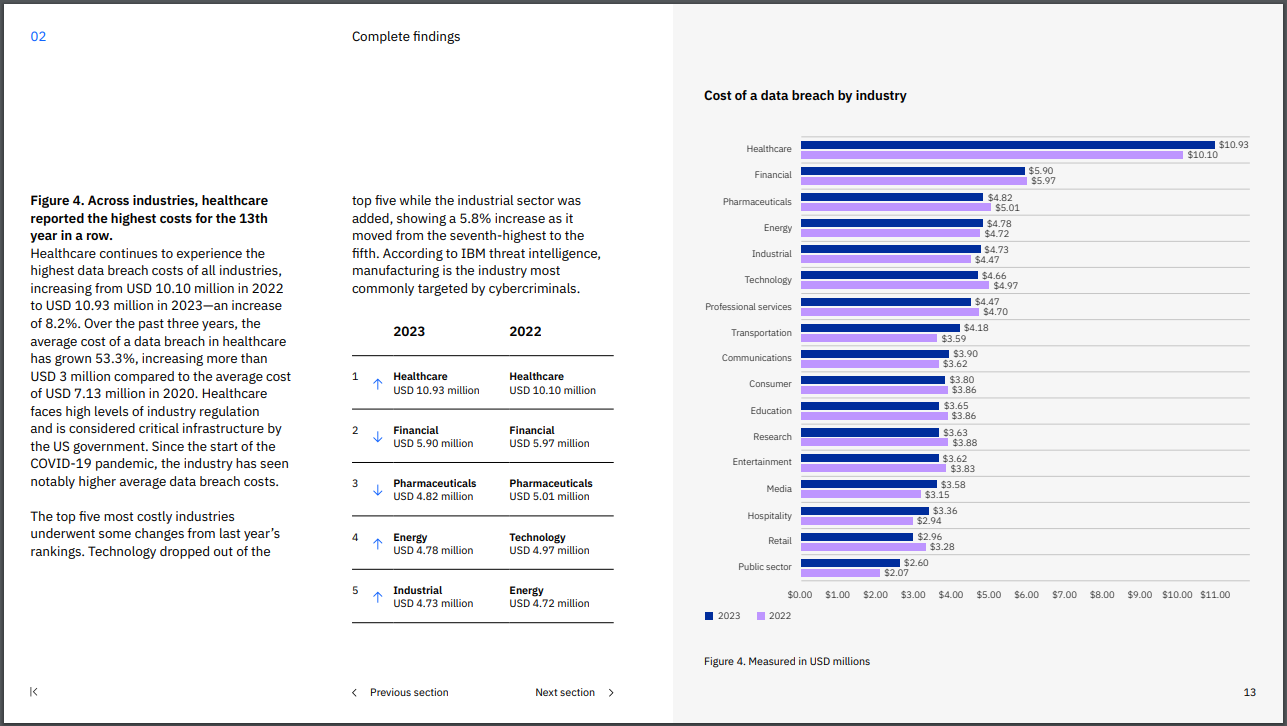
[Caption: Screenshot from IBM's "Cost of Data Breach Report"]
There’s no doubt that data breaches are costly to companies. But how costly are they?
Depending the size of your company, the nature of the cyber attack, the country where the breach occurs, and several other unique factors, the cost of a data breach varies.
However, IBM conducts an annual Cost of Data Breach Report to highlight the funds wasted due to inadequate security and lack of mitigation measures.
Here are some of the stats from that report:
- According to IBM’s report, 2023 met a record high with the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.45 million USD—a 2.3% increase since 2023
- 51% of businesses plan to increase security measures as a result of these threats
- Security AI and automation helped companies reduce data breach costs by $1.76 million USD
- Healthcare data breaches saw a 53.3% increase in data breaches since 2020 spending nearly $11 million USD in total
- 82% of data breaches happened with data stored in a cloud whether personal, private, or multiple environments
- The United States experienced the most costs in data at $9.48 million USD in 2023
- 16% of data breaches were results of phishing attacks while 15% were results of compromised credentials—stolen or compromised credentials took nearly 11 months to identify and resolve
- Only 33% of cyber attacks were identified by internal tools and security teams
These are just a few of the facts about how vulnerable organizations can be without proper workspace security. Read IBM’s full report to help your company stay more informed.
What is Patch Management?
Patch management is the systematic notification, identification, deployment, and verification of updates to software and systems. These updates, or "patches," are designed to correct vulnerabilities, fix bugs, or enhance functionality.
Given the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, understanding the role and lifecycle of these patches is pivotal for maintaining digital security.
What is Patch Management in Cyber Security?
Patches play a defensive role in cybersecurity, acting as immediate fixes to vulnerabilities that could otherwise be exploited by cybercriminals. They are often released in response to the discovery of security weaknesses that pose risks to users and systems.
By applying these patches, organizations and individuals can close security gaps, mitigate risk, and enhance the overall resilience of their digital infrastructure against attacks.
The Lifecycle of a Software Vulnerability
The lifecycle of a software vulnerability begins with its discovery, either by cybercriminals, researchers, or the software's developers. Once identified, the vulnerability is analyzed, and a patch is developed to fix the issue. This patch is then tested and released to the public.
The final stages involve the deployment of the patch by users and continuous monitoring for any new vulnerabilities that may arise. This cyclical process underscores the dynamic nature of cybersecurity and the ongoing need for vigilance.
The Connection Between Patch Management and Cybersecurity
Patch management is intrinsically linked to cybersecurity.
Effective patch management strategies ensure that vulnerabilities are promptly addressed, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit these weaknesses.
It involves not just the application of patches but also:
- Monitoring patches releases
- Prioritizing patches based on the severity of vulnerabilities
- Ensuring minimal-to-no impact to infrastructure when applying patches
- Verifying the successful implementation of patches to ensure no new vulnerabilities are introduced in the process
Patch management reflects an organization's commitment to proactive defense, minimizing the risk of cyber attacks by keeping software and systems up to date.
By understanding and implementing effective patch management processes, businesses and individuals can significantly enhance their protection against the myriad of cyber threats in the digital world.
The Importance and Benefits of Patch Management
There will always feel like there isn’t enough time, resources, or manpower to manage patches and updates properly. But why cut corners if it places the company’s hard work on the line?
As challenging as the process is, proper patch management comes with a wealth of benefits.
Enhances Security
One of the primary reasons for patch management is to enhance the security of systems and networks. Patches tend to address vulnerabilities easily exploitable by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive data, or cause disruptions.
By applying patches, organizations can close security gaps and protect themselves against potential attacks.
Prevents Exploitation of Known Vulnerabilities
Cybercriminals frequently target known vulnerabilities in software and operating systems. Patch management ensures that these known vulnerabilities are fixed as soon as a patch is available, reducing the risk of being targeted by attackers exploiting these weaknesses.
Maintains System and Application Functionality
Apart from security fixes, patches can also include improvements and bug fixes that enhance the functionality and stability of systems and applications. Regular patch management ensures that software runs efficiently and remains compatible with other systems and devices.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the protection of sensitive data and the maintenance of secure systems. Effective patch management is often a key component of compliance strategies, helping organizations meet legal and regulatory standards that protect customer and company data.
Protects Against Malware and Ransomware
Malware and ransomware often exploit vulnerabilities in unpatched systems to infect and spread across networks. Patch management plays a vital role in preventing such infections by ensuring that systems are not susceptible to known types of malwares and ransomware, thereby safeguarding data and ensuring business continuity.
11 Patch Management Challenges You Might Face
Patch management is crucial for many organizations, so why do many hesitate when testing and deploying patches? There are many reasons that might get in the way of your company taking the proper patch management security measures.
Here are some challenges you and many other organizations might face:
- Complex IT environment
- Compatibility issues
- Resource constraints
- Patch prioritization
- Automated vs. manual patching
- Downtime and productivity impact
- Keeping up with vulnerabilities
- Regulatory compliance
- Remote and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies
- Security vs. Usability
- Large end user base
With a wide variety of devices, operating systems, and applications, each requiring its own set of patches, navigating these waters can be tricky. However, rapid patch deployment is essential for safeguarding against vulnerabilities, yet if done without proper testing, it could destabilize your systems.
Identify potential weak areas that might impede your patch management strategies. Once you discover those weak points, you can start working on ways to resolve them.
5 Best Practices for Strong Patch Management

Now that we know the benefits of patch management, and the challenges that might interrupt taking these security measures, how can you improve your mitigation tactics?
Developing a robust patch management strategy is essential for safeguarding your organization's digital assets and ensuring the smooth operation of IT systems.
Here are five ways to build an effective approach.
1. Prioritizing Patches Based on Criticality
Not all patches are created equal. Some address critical vulnerabilities that could be exploited to cause significant harm, while others may offer minor improvements or non-security related fixes. Assessing the criticality of each vulnerability and prioritizing patches accordingly is crucial. This ensures that the most dangerous vulnerabilities are remedied first, reducing the potential impact on your organization.
2. Testing Patches Before Deployment
Before widespread deployment, it’s vital to test patches in a controlled environment. This step helps identify any issues that could disrupt system functionality, allowing IT teams to mitigate problems before they affect the entire network.
3. Automated Patch Management Software and Tools
Automation plays a key role in streamlining the patch management process. Automated tools can help in detecting the need for patches, deploying them across various systems, and ensuring that all devices are consistently up to date. These patch management software and tools save time and reduce the likelihood of human error.
4. Patch Management Policies and Procedures
Establishing clear policies and procedures for patch management is necessary for consistency and compliance. These guidelines should outline how patches are evaluated, tested, deployed, and documented within the organization.
5. Monitoring and Reporting on Patch Status
Continuous monitoring and reporting are essential for maintaining visibility into the patch status of all systems. Keeping track of which patches have been applied—and which have not—helps in identifying vulnerabilities and ensures accountability within the patch management process.
By focusing on these key aspects, organizations can develop a comprehensive patch management strategy that not only protects against cyber threats but also ensures the integrity and reliability of IT systems.
Test Patches Against Your Custom Infrastructure by Using Rimo3
Using Rimo3’s patented automation platform, testing security patches and updates no longer takes weeks or months.
IT managers and enterprise companies can build Rimo3’s technology into their own ITSM process. They can integrate with products like ServiceNow, Microsoft Intune, Nerdio, VMWare, and Liquidware to provide impressive results for deploying updates when they become available.
Stay up to date like never before and let Rimo3 help you secure your Windows estates with confidence.